Yogurt Production
08/08/2014

Yogurt Production
Indian yogurt industry is growing at a compound annual growth rate CAGR of 40-45 percent annually. In 2013 statistics report submitted by ASSOCHAM the Indian yogurt industry was of 750cr in which is estimated to reach 1250cr in 2015. Hence, this statistics describe that how the demand of the packaged yogurt increased and also expected to rise. Today the consumers are more conscious about the health issue and therefore they concerned about hygiene, fat & nutritional contents which may resultant to tremendous rise of the Indian yogurt industry.
Yogurt production process is very interesting and can be done by 2 methods.
1. Set Yogurt Production Procedure
In this process the gel is prepared while by increasing the dryness of the yogurt. During the production process the milk will be thermised and cooled with containing an adequate fat content. The solid part is standardized in mixing line with an addition of dairy ingredients and required additives after which the mixture is mixed slowly with avoiding the air contact into the mixture.
Once the mix is obtained, air is removed and the mix is heated to 65-70ºC followed by homogenisation at 200/250 bar over one or two stages. It is then pasteurised at 95ºC for 300 seconds, after which it is cooled to between 4-6ºC and stored.
In the next phase the flavours are added to the storage tank and are agitated till it properly mixed.
The mixture is pumped through a plate heat exchanger which heats the milk to 45ºC and immediately packaged. The product is subsequently sent to the fermentation chamber where it remains for between 2.5 hours and 3 hours, depending on the final pH. It is then quickly cooled by forced air to 15ºC in another chamber before finally entering the final storage tank at 4ºC where it remains until the following day to be removed.
2. Whipped Yogurt production process
Whipped yogurt is a variation on traditional yogurt made with a process that increases its air content which gives it a lighter texture. This kind of yogurt is sometimes serves as a topping for other types of desert.
The milk, having been thermised and cooled and containing the adequate fat content, has its solids standardised in a mixing line in which powdered milk along with other necessary dairy ingredients and required additives are added. It must be mixed slowly, always avoiding the introduction of air into the mixture.
Once the mix is obtained, air is removed and the mix is heated to 65-70ºC followed by homogenisation at 200/250 bar over one or two stages. It is then pasteurised at 95ºC for 300 seconds, after which it is cooled to 38-42ºC and moved to the fermentation tanks where the culture is added. It is agitated well to obtain a complete mix (This may also be done with an in-line mixer)
Once obtained, the agitation ceases in order to allow the milk to rest during the fermentation period. This period will vary according to the culture used – between 6 and 8 hours.
At the end of fermentation, which is measured by pH, the formed coagulant is gently agitated and moved, via a positive displacement pump with progressive cavity, to a plate cooler in order to be quickly cooled to 20ºC and then stored in a new tank before being transported to the packager.
Prior to packaging, the fruit, pulp and/or marmalade is, continuously and in line, added. Once packaged, the product is placed in a chamber where it is cooled quickly to 12-15ºC with forced air before passing to another chamber to be cooled to 4ºC.
INOXPA offers a wide variety of solutions for the Dairy Industry such as dairy product manufacturing plants, pasteurizers, blenders, milk reception units, valve manifolds, heat exchangers, agitators, etc.
Contact
Other news
-
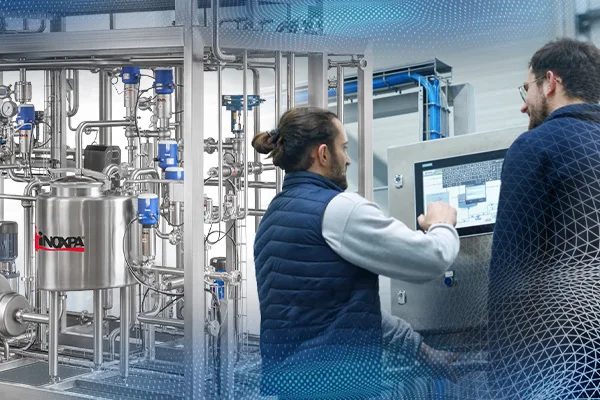 30/07/2025
30/07/2025Integral solutions that make the difference
INOXPA have been offering complete, customised solutions for years. We take care of the entire engineering, automation and assembly process.
Systems -
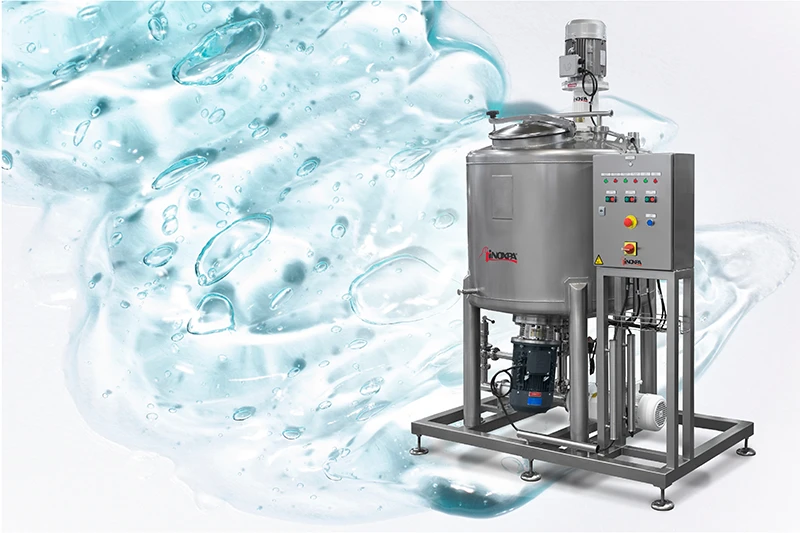 09/07/2025
09/07/2025CMC mixing systems
INOXPA’s CMC mixing systems are efficient, versatile, and customisable solutions for the dispersion of hydrocolloids across various industries.
Systems -
 16/06/2025
16/06/2025U-Stamp certification
This certification strengthens our position as a trusted supplier in industries where quality and compliance with standards is essential.




